Specialista in Ginecologia e Ostetricia
BruceBlaus / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)

amniocentesi, villocentesi, cromosomi https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c7/Human_male_karyotpe_high_resolution_-_Chromosome_X.png

BruceBlaus / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
INVASIVE PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS
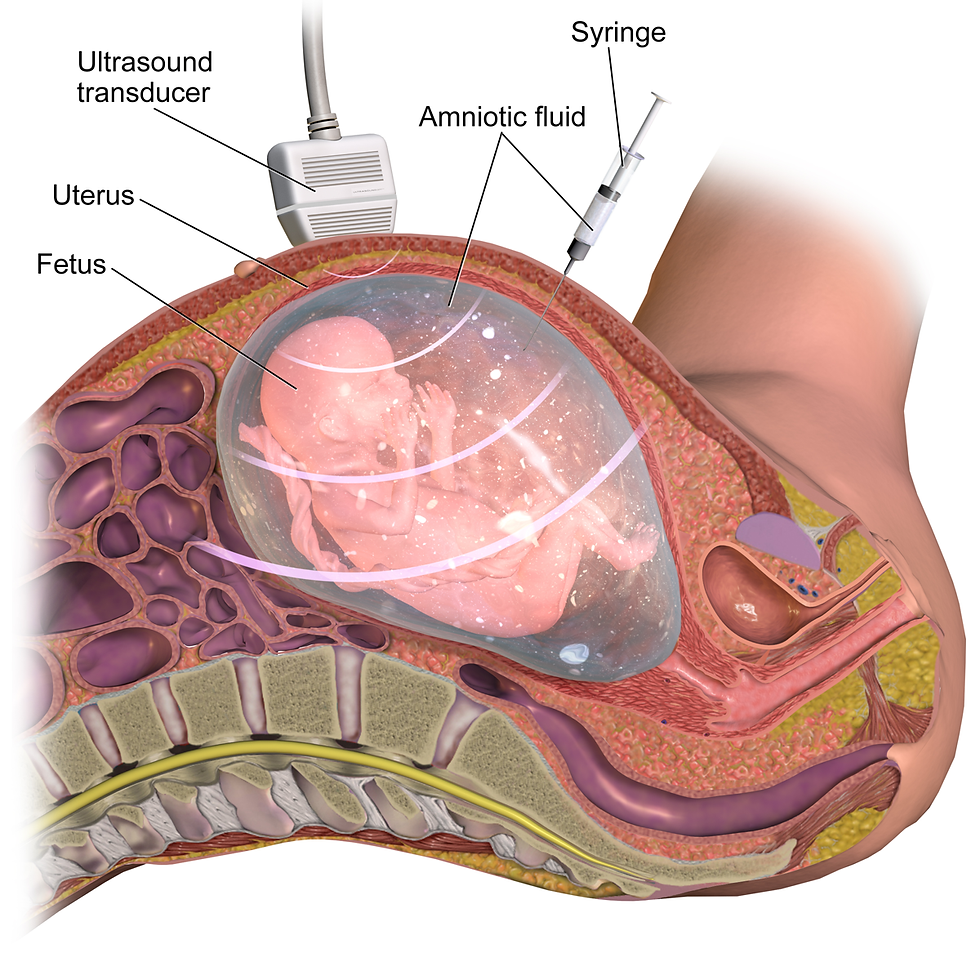
Amniocentesis is the most widely used invasive prenatal diagnosis technique, aimed at the acquisition, through a transabdominal puncture, under ultrasound control, of the amniotic fluid, ideally around 16 weeks of amenorrhea. The risk of abortion, connected to the invasiveness of the technique, is calculated in about 1: 200. The amniotic fluid contains a corpuscular part formed by cells that derive from the fetus (skin, mucous membranes, genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal system). These cells are used for cytogenetic investigations, and possibly for molecular and biochemical analyses, both directly and on cultured cells.
Chorionic villus sampling is an invasive technique, used for the collection of the trophoblast, by transabdominal puncture, under ultrasound control, ideally around10-12 week of amenorrhea. The risk of abortion, related to the invasiveness of the technique, is around 2-3%. The acquired tissue can be used for cytogenetic analysis. The advantage of the earliness of the technique, compared to amniocentesis, is offset by its greater invasiveness and the acquisition of placental and non-fetal tissue.
